Measurement can be a difficult concept, especially for young students. Based on conversations from previous classes, we have discovered that students learn best when concepts are taught in a real world context. Teachers should focus on hands on activities to give students experience using measurement rather than just showing pictures and assigning worksheets. (Van de Walle, pg 369)
- · Describe everything you know about “standard units of measure."
- Give examples of how you have used standard units of measure at home in the last week.
- Give examples of how you have used non-standard units of measure at home in the last week.
- Why is it important to have a standard system of measurement?
The three steps of Measurement
- Make a Comparison
- Concrete examples
- Use of tools
The Four Things we Measure
- Time
- Mass
how many molecules (it is NOT weight).
it is consistent - Distance or Length
- Volume
how much space it takes up
Geometry
- Geomoetry is a vocabulary course.
- Very important to know the definitions
Perpendicular lines
The slopes are the negative reciprocal of each other.
Examples:
Transversal
- in class we talked about transversal being any line that intersects any set of parallel lines. The transversal line does not have to be perpendicular.
Practice Drawing using verbal clues:
Supplementary
- two angles that add up to 180
- "supplementary makes a sunrise"
Complementary
- two angles that add up to 90
- "Compliments cause love, and love starts with an L"
Triangles:
Finding how many angles are in a triangle
This activity proves that there are 180 degrees in a triangle.
Vertical Angles
Interior Angles
Exterior Angle








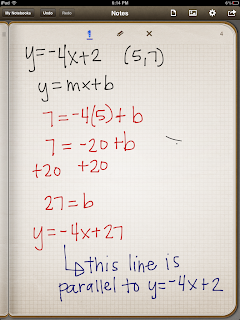











No comments:
Post a Comment